Traditionally seen as an extra step after buying a product or service, insurance can today be seamlessly blended into them, which results in a frictionless customer experience and significant benefits for insurers and non-insurance businesses.
This is called embedded insurance, with its market currently valued at $90,570 million and projected to rise at a CAGR of 11.6% from 2025 to 2033, according to the Market Report Analytics.
What is embedded insurance? How does it work? What benefits does it deliver to businesses? Read on to find answers to these and other questions.
What Is Embedded Insurance?
Embedded insurance refers to integrating coverage directly into the purchase of a non-insurance product or service, like booking a flight with a travel insurance option at checkout or buying a new phone with an opportunity to add accidental damage cover.
The idea is pretty simple: insurance becomes part of the transaction rather than an extra step. Businesses partner with insurers behind the scenes, so the offer appears naturally in the course of the customer journey. The policy is still underwritten by a licensed insurer, but the buyer experiences it as a part of their purchase, without any complex forms or long conversations. It’s convenient for customers and offers clear benefits for businesses, so it’s little wonder this model is getting so much traction.
How Embedded Insurance Works
In most cases, businesses selling products or services work with insurers through APIs. The process is invisible to the customer, who experiences it as an extra option added to checkout — they choose a product, see an offer of protection connected to it, and decide whether to accept. When the customer opts to add insurance, the API communicates with the insurer’s platform, confirms eligibility, generates the terms, and attaches the policy to the purchase in real time.
Embedded Insurance vs. Traditional Insurance
Traditional insurance is purchased as a separate product. Policyholders compare providers, review policies, and complete applications. Once the paperwork is done, coverage starts, but the steps can take time and require effort from the customer.
In contrast, embedded insurance is offered at the very moment of purchase, when a customer books a trip, rents a car, or signs up for a digital service. Instead of browsing through multiple providers, the option is already built into the checkout flow. The policy is issued with a single click as seen by the customer — all the administrative work is handled by the systems linking the business to the insurer.
Obviously, embedded coverage beats the traditional approach from the perspective of the customer experience, as demonstrated by PwC’s recent study showing that 60% of consumers are open to embedded insurance.
Insurers also see a major difference — selling traditional insurance requires a dedicated distribution channel and sales teams, while embedding uses the existing sales process of another product.
For non-insurance businesses, the contrast is just as clear. Unlike with traditional insurance, they don’t need to refer their customers elsewhere — protection becomes part of their existing sales flow.
Real-World Examples of Embedded Insurance
Travel bookings
Travel providers were among the first to adopt embedded insurance. The risks of delays, cancellations, medical emergencies, and lost luggage are directly connected to the booking. Adding coverage during checkout saves travelers from the hassle of finding a separate policy.

For example, Skyscanner partners with Cover Genius to provide tailored travel insurance options within its booking flow.
Electronics and retail
When buying electronics or household appliances, customers often think about what happens if the item breaks or fails. Embedding protection at the point of sale makes sense because it addresses that concern at the moment of purchase. Instead of sending buyers to a warranty provider’s website, the retailer can complete the process in seconds during checkout.
One example is Amazon, which offers extended protection plans for devices and appliances at the time of purchase, backed by Asurion. Online shoppers can add coverage for mechanical breakdowns or accidental damage with a single click.
Mobility and sharing economy
Platforms built on short-term use or sharing models rely on trust. Insurance embedded directly into the transaction fills gaps that personal policies rarely cover. For drivers, passengers, and hosts, this protection is what makes these platforms workable at scale.
For instance, Uber provides automatic injury and liability coverage for drivers and riders, while Airbnb’s AirCover covers hosts at no extra cost.
Fintech and neobanks
Digital banking apps embed insurance into cards and accounts, creating a stronger value proposition. Card protection, travel insurance, or purchase coverage are often found as parts of modern digital banking products.

An example here is Revolut, which includes travel protection as part of its paid account tiers. Customers who subscribe to the Metal or Ultra plan receive insurance automatically bundled into their banking package.
Delivery and return protection
Buying online often creates uncertainty around shipping or returns. Embedded insurance can be used to cover risks like packages lost in transit or the cost of sending items back. Marketplaces benefit by removing friction from the decision to buy, while customers gain confidence that problems will be handled smoothly.
Sure’s Retrace is a clear example, offering return-shipping protection that retailers can add to checkout.
Benefits for Consumers
Seamless experience with zero friction
Instead of searching for a provider and then filling out forms, consumers are offered coverage at the exact moment of purchase. It requires a click to confirm, making insurance feel like another step in the transaction rather than a separate task.
Personalization and flexibility: only pay for what you need
Unlike traditional policies that often bundle a wide range of protections, embedded insurance is usually tied to a specific purchase, without paying for services you don’t use. You pay for ski trip coverage only when you book the trip, or for delivery protection only when you order a high-value item.
Embedded insurance as a natural extension of the purchase journey
Embedded insurance feels like a feature that belongs to the product itself, such as buying a new phone with optional damage cover or reserving a rental car with built-in liability protection.
Peace of mind without paperwork or extra effort
Consumers often associate insurance with documents and back-and-forth communication with an insurance agent. Embedded insurance removes much of that perception. Activation happens instantly, policy details are stored digitally, and claims are automated through the same platforms customers already use.
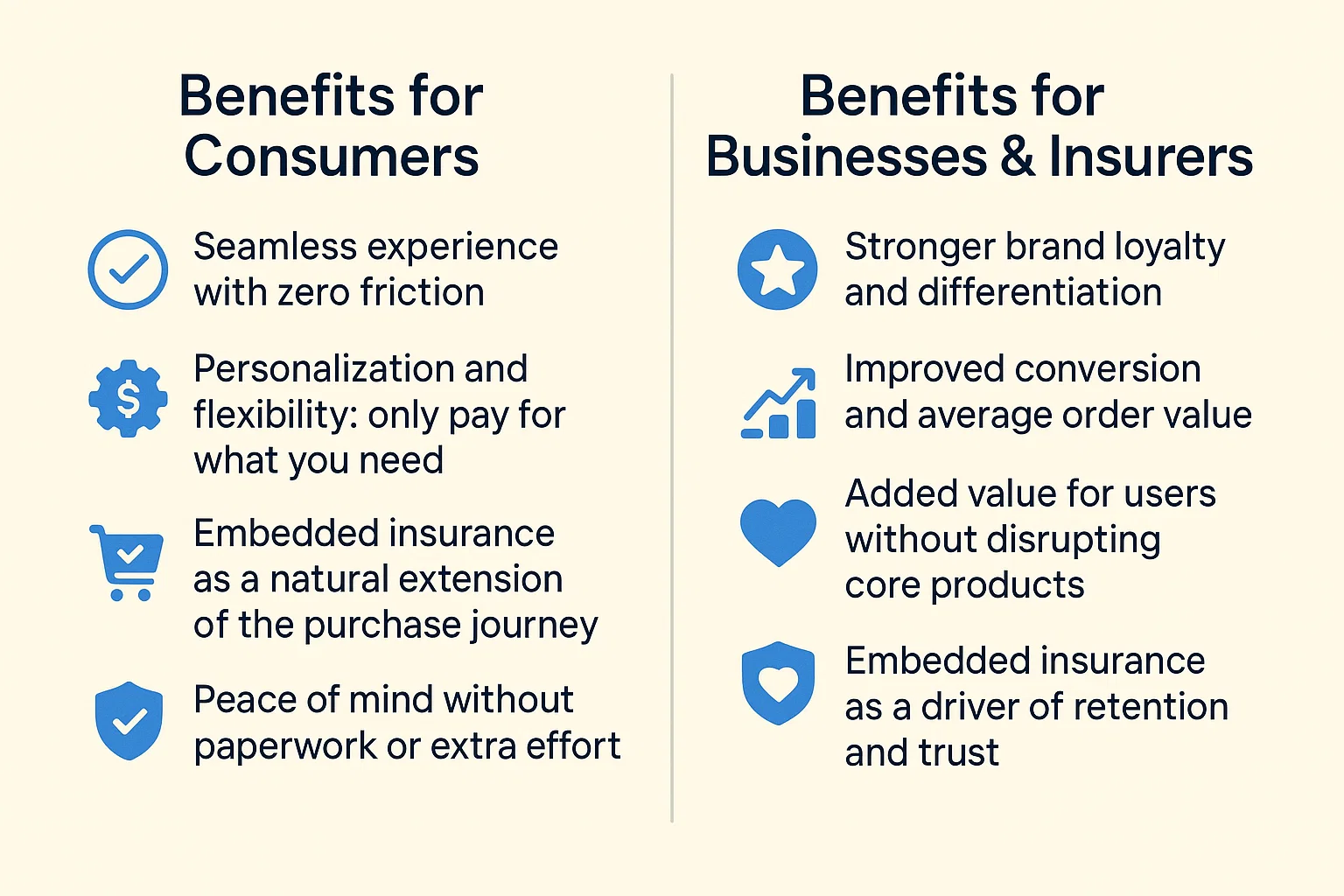
Benefits for Businesses & Insurers
New sales channels and extended reach
Insurers have historically relied on agents, brokers, advertising, outbound sales teams, and third-party affiliates to connect with potential buyers. With embedded coverage, they can tap into existing user bases with no need to build traditional sales pipelines. Retailers, travel sites, mobility services, and fintech apps act as insurance distribution partners. By allowing insurers to reach their customers, these businesses also create an additional revenue stream for themselves.
Stronger brand loyalty and differentiation
Offering built-in protection helps businesses stand out from competitors who don’t. This signals care for the customer’s safety and strengthens loyalty over time. An embedded insurance company, in turn, can benefit from being associated with trusted brands that already own strong customer relationships.
Improved conversion and average order value
When protection products are offered together with the main purchase, customers are more likely to accept them. Insurance appears at the moment when it feels relevant, for example, weighing the risk of a delayed flight or a cracked phone screen. On top of that, it doesn’t require much effort to accept the offer, which translates to higher conversion rates. Order values grow, since the insurance premium is added to the base transaction. At the same time, embedded insurance providers capitalize on selling policies at scale with less friction.
Added value for users without disrupting core products
Customers experience embedded insurance as a bonus, without being distracted from their purchase journey. The protection feels like part of what they actually planned to buy, allowing businesses to deliver extra value while keeping the primary product intact.
Embedded insurance as a driver of retention and trust
Embedded insurance solutions show customers that their risks are considered and addressed upfront. This goes a long way toward building trust and encouraging repeat purchases.
Technologies Powering Embedded Insurance in 2025
Now that we’ve taken a detailed look at the business benefits of embedded insurance products, let’s explore the technology that runs behind the scenes to make it possible.
APIs
Application Programming Interfaces, or APIs, link insurance platforms with retailers, banks, travel sites, and mobility services. Policies are priced and issued in real time, without the need for manual steps.
Artificial intelligence and machine learning
By analyzing customer behavior and purchase history, algorithms can tailor offers to match the actual needs of insurance consumers. Machine learning automates claims processes, reducing human intervention and shortening resolution times.
Data and analytics
Access to transactional and behavioral data lets insurance providers adjust coverage based on what customers are doing at that moment. Advanced analytics make it possible to design relevant and cost-effective policies.
Cloud infrastructure
The technical demands of embedded insurance call for systems that can handle scale and respond instantly. Cloud platforms provide that, allowing insurers and their partners to deploy new products quickly, manage peaks in demand, and securely store sensitive customer data.
Digital identity and payments
Last but not least, authentication and payments close the loop. Digital identity solutions confirm who the buyer is, while embedded payment technologies ensure that premiums are collected as part of the main transaction.
Why IT Companies Should Pay Attention
The number of non-insurance businesses looking to leverage digital embedded insurance is growing, which also means increasing demand for technical expertise. For IT companies, this is a chance to expand their role. They can become the partners who connect insurers with distribution platforms, building the infrastructure for embedded insurance.
Conclusion
With the impressive benefits it offers, embedded insurance is set to become more common in the next few years. For businesses and insurance providers, implementing it is a great opportunity to stand out from the competition and reach new audiences.
If you’re an insurance business looking to introduce digital solutions, TechVision can help. We have extensive experience in insurance software development and legacy systems modernization, so feel free to contact us and discover how we can take your operations to the next level.